Optical illusions are more than just a fun way to pass the time; they offer a fascinating glimpse into how our brains work. These visual puzzles challenge our perception and can reveal surprising aspects of our personalities.
Optical illusions occur because the brain sometimes misinterprets the information received from the eyes. This can happen when the eyes send conflicting signals, leading the brain to perceive things differently from reality.
Take a look at the image below. What do you see first: an eaten apple core or two faces? Your initial response can reveal a deep secret about your personality.
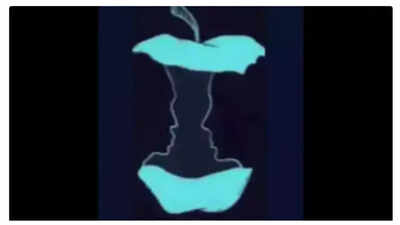
This intriguing illusion was shared on social media by Marina Winberg. According to Winberg, "This image is a classic dual-illusion where you can either see two faces (a man and a woman) looking at each other OR an apple core—what you notice first says a lot about your mindset!"
What was your initial perception?
If the first thing you noticed was two faces, it suggests that “You’re a logical, analytical thinker with strong morals. You think before you act, value stability, and solve problems creatively— but sometimes, curiosity gets the best of you!”
If your eyes were immediately drawn to the apple core, it indicates that “You’re intuitive, emotionally aware, and great at reading subtle cues. You know the right thing to say, but often stay quiet. Stability matters to you, and you protect what’s important.”
Optical illusions are categorized into three main types:
Literal Illusions: These illusions occur when the brain pieces together elements of an image to create a perception that isn't actually there. The apple/faces illusion falls into this category.
Physiological Illusions: These arise from overstimulation of the visual system. Exposure to intense light, movement, or color can lead to afterimages or motion illusions.
Cognitive Illusions: These illusions are based on the brain's subconscious interpretations. The Müller-Lyer illusion, where lines appear to be different lengths due to surrounding shapes, is a prime example.
Newer articles
Older articles
 Black Caps Announce Packed 2025-26 Home Schedule Featuring Australia, England, West Indies & South Africa
Black Caps Announce Packed 2025-26 Home Schedule Featuring Australia, England, West Indies & South Africa
 Jaiswal Aims to Eclipse Gavaskar's 49-Year-Old Record as India Seeks Series Leveler at Edgbaston
Jaiswal Aims to Eclipse Gavaskar's 49-Year-Old Record as India Seeks Series Leveler at Edgbaston
 Rishabh Pant: Greg Chappell Lauds Indian Star's Game-Changing Cricket Revolution
Rishabh Pant: Greg Chappell Lauds Indian Star's Game-Changing Cricket Revolution
 Samsung Unveils Galaxy A35 5G and A55 5G Pricing, Specs, and Availability
Samsung Unveils Galaxy A35 5G and A55 5G Pricing, Specs, and Availability
 5 Silent Signals: Spotting Prediabetes Without a Blood Test
5 Silent Signals: Spotting Prediabetes Without a Blood Test
 Cummins Lauds Australia's Solid Start in New World Test Championship Campaign
Cummins Lauds Australia's Solid Start in New World Test Championship Campaign
 Science-Backed Strategies: 5 Simple Habits for a Healthier Heart
Science-Backed Strategies: 5 Simple Habits for a Healthier Heart
 Anish Giri's Jesting Remark Highlights Praggnanandhaa's Rise to Top Junior Chess Ranking
Anish Giri's Jesting Remark Highlights Praggnanandhaa's Rise to Top Junior Chess Ranking
 India vs England: Calls Mount for Kuldeep Yadav's Inclusion in Edgbaston Test Amid Strategic Reworking
India vs England: Calls Mount for Kuldeep Yadav's Inclusion in Edgbaston Test Amid Strategic Reworking
 The subtext of Gill's selection
The subtext of Gill's selection